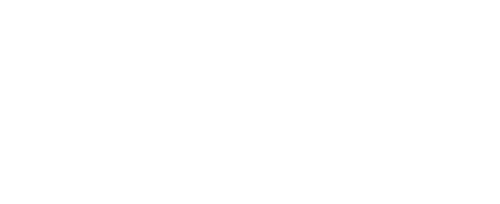
Example 14: deri_speccond, specific conductivity
This equation permits conductivity readings taken in different environments to be compared by correcting them to a standard environment at 25°C. Specific conductivity is usually of greater interest in fresh water applications, and is by convention always reported in μS/cm, although the parameter does apply to salt water as well. The equation which corrects for temperature to derive specific conductivity from standard conductivity is given below. It is associated with the scon00 derived channel type.
where
Ccorr is the standard conductivity reading (already compensated for temperature dependence of the measurement circuit as described in Example 4),
T is the temperature used for correction, in °C,
K0 is a units correction factor, and
K1 is a temperature coefficient.
In the calibration settings for the scon00 derived channel type, the channel cross-reference index for Ccorr is given by n0, and for T by n1.
K0 has a value of 1 if the Ccorr channel is in μS/cm, or a value of 1000 if Ccorr is in mS/cm. The logger can deduce this from the units of the Ccorr channel; an explicit coefficient is not needed.
K1 depends on the ionic composition of the water being monitored, and typically has a value in the range 0.0191 to 0.0214. The lower end of this range is suitable for KCl solutions, the higher end for NaCl solutions. The value used by the logger can be queried and modified via the settings command, using the speccondtempco parameter. If this parameter is never explicitly set, the default value used is 0.0191.